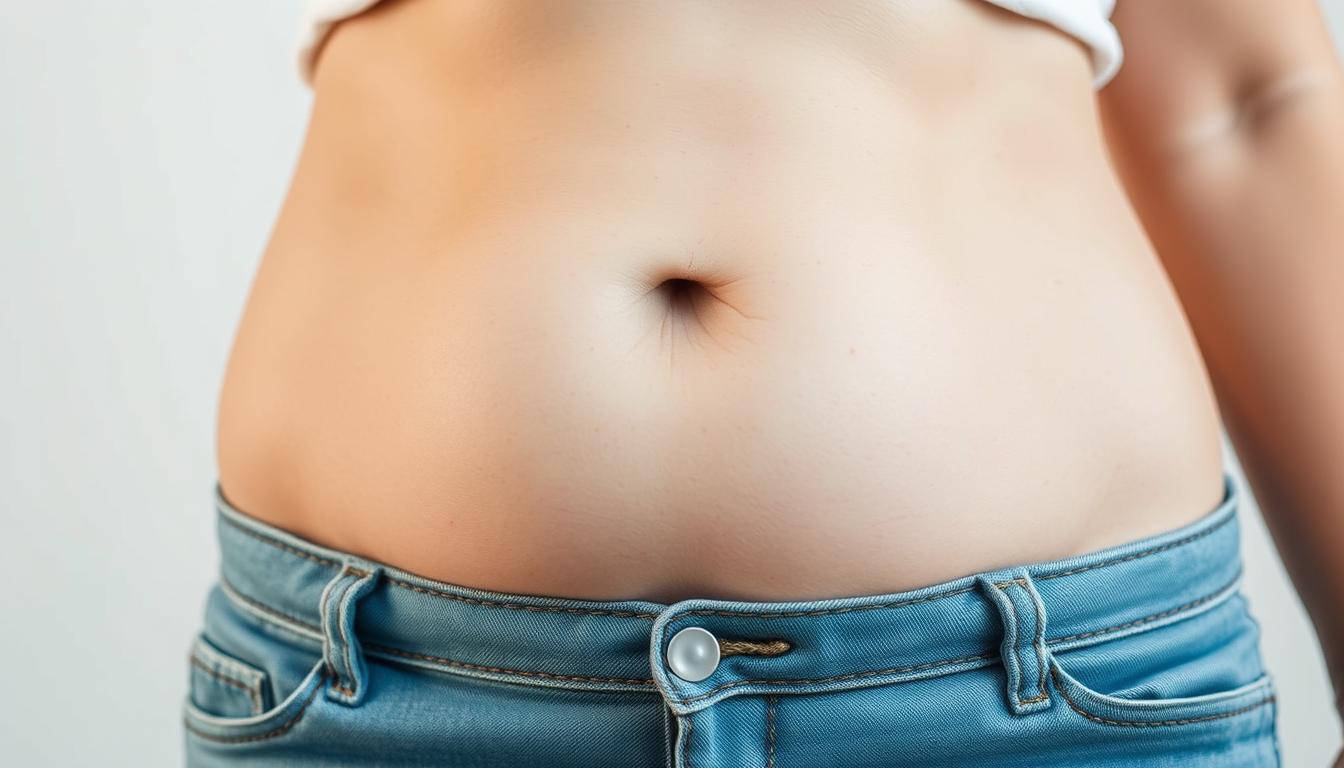
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a complex hormonal condition. It affects many women worldwide. The “PCOS belly” is a noticeable symptom. It’s a unique weight distribution that can affect a woman’s health and appearance.
 alt=”What Does A PCOS Belly Look Like” data-id=”147933313″ />
alt=”What Does A PCOS Belly Look Like” data-id=”147933313″ />
PCOS leads to hormonal imbalances. This can cause weight gain, especially around the midsection. The weight gain is due to hormones, insulin resistance, and other factors.
Knowing the signs of a PCOS belly is key. It helps women with this condition take steps to improve their health.
Key Takeaways
- PCOS is a hormonal condition that can lead to a distinctive “PCOS belly” appearance
- The PCOS belly is characterized by excess weight gain, particularly in the abdominal area
- Understanding the symptoms and signs of a PCOS belly is crucial for effective management of the condition
- PCOS-related weight gain is often the result of hormonal imbalances and insulin resistance
- Recognizing the unique characteristics of a PCOS belly can help women take proactive steps to address this aspect of the condition
What is PCOS?
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a condition that affects how a woman’s ovaries work. It happens when hormones like estrogen and testosterone are out of balance. Women with PCOS might have irregular periods, extra hair growth, or trouble losing weight. Sometimes, small cysts form on their ovaries, but not always.
PCOS is common and can affect your health in different ways, from skin issues to difficulties getting pregnant. The earlier you understand it, the easier it is to manage.
Understanding PCOS and Its Impact on Body Shape
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a complex hormonal disorder. It affects a woman’s reproductive health and body shape. Hormonal imbalances and their effects on metabolism and fat distribution are at the heart of this condition.
What Does a PCOS Belly Look Like?
A PCOS belly is usually a result of weight gain, especially around the stomach area. The weight doesn’t always spread evenly. Instead, it collects in the middle, giving the stomach a round or bloated look. This is called abdominal fat.
It’s not just about appearance—this kind of fat can be linked to health problems like diabetes or heart disease if not managed well.
The Role of Hormones in PCOS
PCOS is marked by too much androgens, or male hormones, in women. This imbalance causes symptoms like irregular menstrual cycles, acne, and excess facial or body hair growth. It also affects how the body stores and distributes fat, often leading to abdominal fat or a “PCOS belly.”
How Do You Know if You Have a PCOS Belly?
Here are some signs to look for:
- Weight gain around your waist but not in other areas like arms or legs.
- A bloated or puffy stomach, even if you’re not overeating.
- Difficulty losing weight, even with exercise and diet.
If you notice these, it’s a good idea to see a doctor for tests to confirm if PCOS is the cause.
Causes of a PCOS Belly
The main reason for a PCOS belly is hormone imbalance. When your body produces too much insulin, it can lead to weight gain, especially around the stomach.
Other causes include:
- Inflammation: Chronic inflammation can increase fat storage.
- Stress Hormones: High cortisol levels can lead to more fat around the waist.
Risk Factors
Some things make PCOS more likely:
- Family History: If your mom or sister has PCOS, your chances are higher.
- Lifestyle: Poor diet and lack of exercise can make symptoms worse.
- Age: PCOS often shows up in your teens or twenties but can continue later in life.
What Can You Do About It?
There are ways to reduce a PCOS belly and feel better:
- See a Doctor: They might suggest medicine to help with hormones or insulin levels.
- Stay Active: Regular movement can burn fat and improve your mood.
- Sleep Well: A good night’s rest helps balance hormones.
Exercises for a PCOS Belly
Certain exercises work well for reducing belly fat:
- Walking: A simple, low-impact way to burn calories.
- Strength Training: Builds muscle and increases metabolism.
- Yoga: Reduces stress and improves flexibility.
How PCOS Affects Fat Distribution
The hormonal imbalance in PCOS messes with the body’s fat-storing ways. This leads to more fat around the abdomen. Insulin resistance, common in PCOS, makes abdominal fat even more likely.
Common Body Changes with PCOS
- Increased abdominal fat and a distinct “PCOS belly” appearance
- Weight gain, particularly around the midsection
- Difficulty losing weight, despite diet and exercise efforts
- Irregular menstrual cycles and excess facial/body hair growth
- Skin changes, such as acne or dark patches
It’s key to understand how PCOS, hormones, and body shape are linked. This knowledge helps manage the condition and its physical effects.
What Does A PCOS Belly Look Like
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS) is a hormonal disorder. It affects a woman’s body shape and fat distribution. A PCOS belly appearance is a common sign. It often looks like a central obesity or apple-shaped figure.
Women with PCOS often have extra weight around their midsection. This central obesity comes from hormonal imbalances. It makes the body store fat in the belly area.
The PCOS belly looks round and protruding. It has a lot of fat around the waist and belly. This makes the belly feel firm or doughy.
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Fat Distribution | Excess fat around the waist and abdomen, leads to a distinctive apple-shaped figure |
| Abdominal Appearance | Protruding, rounded abdomen with a firm, doughy texture |
| Underlying Cause | Hormonal imbalances in PCOS lead to central obesity and fat storage in the midsection |
Knowing what a PCOS belly looks like is important. It helps women with PCOS spot signs and symptoms. They can then get the medical help they need.
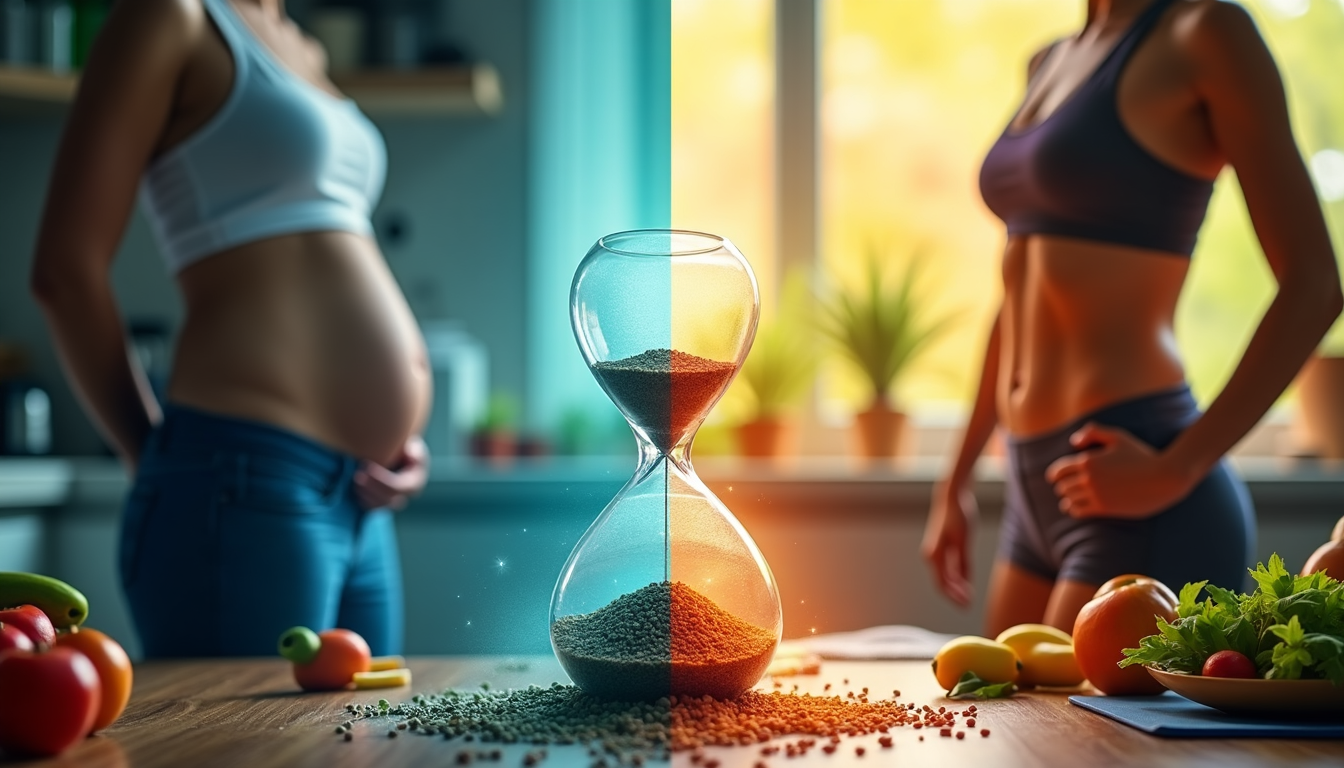
Distinguishing PCOS Belly vs Pregnant Belly
Women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) often wonder if their belly looks like a pregnant woman’s. Both can cause a swollen belly, but they are different.
Key Physical Differences
A PCOS belly is softer and spreads out more evenly. A pregnant belly is firmer, rounder, and sticks out more.
Weight Distribution Patterns
PCOS makes women carry extra weight around their belly, hips, and thighs. Pregnancy makes weight spread out more, with the belly being the biggest part.
Timing and Development
A PCOS belly grows slowly over time because of hormone problems. A pregnant belly grows faster as the pregnancy goes on.
Knowing the differences between a PCOS belly and a pregnant belly helps women manage their health better. They can also get the right medical help.
Common Symptoms Associated with PCOS Belly
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a complex hormonal condition. It can change how a woman’s body looks, especially the belly. People with PCOS often have other symptoms too.
One common symptom is irregular menstrual periods. Women with PCOS might have cycles that are off, missing, or last too long. This can affect their health and ability to have kids. They also often deal with acne, caused by too much male hormone.
Another symptom is hirsutism, or too much hair in places like the face, chest, and back. This is due to hormonal imbalances in PCOS. It can make people feel really upset.
PCOS can also lead to mood changes, like anxiety and depression. These feelings can make life harder. Knowing all the symptoms, including the belly changes, helps get the right treatment.
“Recognizing the various PCOS-related symptoms, in addition to changes in body shape, is essential for obtaining a comprehensive diagnosis and effective treatment plan.”
The Connection Between PCOS and Insulin Resistance
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a complex hormonal disorder. It affects women’s metabolic health. Insulin resistance is a key factor in PCOS. This is when the body’s cells don’t respond well to insulin, leading to blood sugar problems.
Blood Sugar Regulation
Insulin helps keep blood sugar levels healthy. In PCOS, insulin resistance makes the pancreas work hard. It tries to control blood sugar but often fails, leading to high blood sugar levels. This is a risk factor for type 2 diabetes.
Metabolic Impact
Insulin resistance in PCOS can cause big problems. Women with PCOS are more likely to get metabolic syndrome. This is a group of conditions that raise the risk of heart disease and stroke.
Weight Management Challenges
Insulin resistance makes it hard to lose weight in women with PCOS. The body can’t use insulin well, so it stores extra calories as fat. This often shows up as a “PCOS belly.”
| Condition | Prevalence in PCOS | Impact on Health |
|---|---|---|
| Insulin Resistance | 60-90% | Increased risk of type 2 diabetes, metabolic syndrome, and cardiovascular disease |
| Metabolic Syndrome | 30-50% | Elevated risk of heart disease, stroke, and other chronic health issues |
It’s important to tackle insulin resistance in PCOS. This can help manage the condition and its risks. By making healthy lifestyle choices, like eating right and exercising, women with PCOS can improve insulin sensitivity. This helps control blood sugar and supports overall health.
PCOS Belly vs Normal Belly: Identifying the Differences
It’s hard to tell the difference between a PCOS belly and a normal belly. Knowing how fat is stored, how firm it is, and how it looks is important. This helps us see what makes a PCOS belly special.
People with PCOS have more visceral fat. This fat is deep and wraps around the organs inside. It’s bad because it can lead to health problems like insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. On the other hand, a normal belly has more subcutaneous fat. This fat is under the skin and is less active.
| Characteristic | PCOS Belly | Normal Belly |
|---|---|---|
| Fat Distribution | Predominantly visceral fat | Primarily subcutaneous fat |
| Firmness | Firmer, more rigid feel | Softer, more pliable feel |
| Appearance | Rounded, protruding shape | Flatter, less pronounced |
A PCOS belly feels harder and stiffer. This is because the visceral fat is around the organs. A normal belly feels softer because of the subcutaneous fat.
A PCOS belly looks rounder and sticks out more. A normal belly looks flatter and less noticeable. These differences in shape and look can help tell them apart.
“Understanding the unique characteristics of a PCOS belly is essential for effective management and improving overall health.”
Knowing the differences between a PCOS belly and a normal belly helps people understand their body better. They can then take steps to manage their PCOS and feel better overall.
Effective Strategies for Managing PCOS Belly Fat
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a complex hormonal condition. It can make it hard to manage weight, especially in the belly. But, with the right approach, people with PCOS can control their belly fat and get healthier.
Dietary Modifications
Eating a low-glycemic diet is key for managing PCOS. Foods with a low glycemic index, like whole grains and lean proteins, help control blood sugar. They also reduce insulin resistance, which helps with weight gain.
Adding healthy fats, like those in avocados and nuts, helps you feel full. It also helps balance hormones.
Lifestyle Changes
Regular exercise is vital for managing PCOS. Doing both cardio and strength training burns calories and builds muscle. It also improves insulin sensitivity.
Stress management, like yoga or meditation, is also important. It lowers cortisol levels, which helps prevent belly fat.
Medical Interventions
Healthcare providers might suggest medical help for managing PCOS. This could include hormones like metformin or oral contraceptives. They might also recommend insulin-sensitizing drugs or other treatments for metabolic imbalances.
Combining diet changes, lifestyle adjustments, and medical help is the best way to manage PCOS belly fat. It improves overall health.
| Dietary Strategies | Lifestyle Changes | Medical Interventions |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
Using a mix of these PCOS management strategies helps with weight loss. It also manages PCOS belly fat for better health and well-being.
The Impact of Alcohol on PCOS Symptoms
Living with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a delicate balance. Alcohol can greatly affect PCOS symptoms. It’s important to know how alcohol and PCOS interact to keep hormones balanced and stay healthy.
Alcohol and PCOS have a complex relationship. It affects the liver and hormones like estrogen and testosterone. This can make PCOS symptoms worse, like irregular periods, acne, and weight gain.
Alcohol also messes with blood sugar levels. This is bad for people with PCOS, who often have insulin resistance. The liver and metabolism get stressed, making things harder.
Navigating Alcohol Consumption with PCOS
Women with PCOS should limit or avoid alcohol. Even a little can affect symptoms. If you drink, watch how your body reacts.
Try non-alcoholic drinks instead, like herbal teas or water with fruits. Making healthy choices helps manage PCOS better.
| Impact of Alcohol on PCOS | Recommendations for PCOS Patients |
|---|---|
|
|
Knowing how alcohol affects alcohol and PCOS helps manage the condition. It’s key to tackling liver function and hormonal balance issues caused by alcohol.
PCOS Belly Fat Exercise: Targeted Workout Solutions
Managing PCOS belly fat is tough, but the right exercise can help a lot. For those with PCOS, mixing strength training and cardio is key. It helps cut down belly fat and improves body shape.
Strength Training for PCOS Belly Fat
Strength training is great for the core and belly. Try planks, crunches, and leg raises. They tone your midsection, boost muscle strength, and speed up your metabolism.
- Do 2-3 strength training sessions a week, focusing on the core.
- Do big exercises like squats, lunges, and deadlifts. They burn lots of calories.
- Make your workouts harder and longer to keep seeing results.
Cardiovascular Exercise for PCOS Belly Fat
Cardio is also super for losing belly fat with PCOS. Try brisk walking, jogging, cycling, or swimming. They burn calories, help with insulin, and aid in weight control.
- Do 150-300 minutes of moderate cardio a week, or 75-150 minutes of hard cardio.
- Change up your cardio to keep it interesting and avoid getting stuck.
- Try HIIT workouts for extra fat loss in the belly.
Being consistent is crucial for fighting PCOS belly fat with exercise. Mix strength and cardio in your routine. Be patient as your body gets better.
| Exercise Type | Benefits for PCOS Belly Fat | Recommended Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Strength Training | Tones and tightens abdominal muscles, boosts metabolism | 2-3 sessions per week |
| Cardiovascular Exercise | Burns calories, improves insulin sensitivity, promotes weight management | 150-300 minutes of moderate-intensity or 75-150 minutes of vigorous-intensity per week |
Natural Remedies and Supplements for PCOS Management
Managing PCOS can be tough. But, using natural remedies and supplements might help a lot. These can include herbal solutions and vitamins. They can help with the hormonal and metabolic problems of PCOS.
Herbal Solutions
Some herbs might help with PCOS symptoms. Inositol, Cinnamon, and Chasteberry are examples. They might make insulin work better, help with menstrual cycles, and balance hormones.
- Inositol, a B vitamin, can help with ovulation and lower androgen levels in PCOS women.
- Cinnamon can make insulin work better, which is good for PCOS.
- Chasteberry, or Vitex, might help with menstrual cycles and reduce acne and hair growth.
Vitamin and Mineral Support
Some vitamins and minerals can help with PCOS. Vitamin D is important for insulin and reproductive health. Many women with PCOS have low vitamin D. Taking it might help with metabolism and hormones.
| Nutrient | Potential Benefits for PCOS |
|---|---|
| Vitamin D | Improved insulin sensitivity, reproductive function |
| Magnesium | Enhanced insulin sensitivity, reduced inflammation |
| Zinc | Regulation of androgen levels, improved ovulation |
Before trying natural remedies or supplements for PCOS, talk to a doctor. They can help make sure these are safe and work well with other treatments.
 alt=”PCOS natural remedies” data-id=”147933315″ />
alt=”PCOS natural remedies” data-id=”147933315″ />
Conclusion
The PCOS belly is a sign of a complex hormonal disorder. We’ve learned about hormones and insulin resistance. We also know how to tell a PCOS belly from a pregnant one.
Managing PCOS long-term means tackling the root causes, not just the symptoms. Making diet changes, living healthier, and getting medical help are key. This way, women with PCOS can control their health and feel better.
It’s important to spread the word about PCOS. This helps those affected live better lives. With the right support and care, women with PCOS can reach their health goals and have a brighter future.
FAQ
What is a PCOS belly?
A PCOS belly is when women with PCOS gain weight around their belly. This weight gain is due to hormonal changes. It makes their belly look like an apple.
How does PCOS affect body shape and fat distribution?
PCOS changes hormone levels, especially androgens. This can make fat build up in the belly. So, women with PCOS often have a big belly.
What are the common symptoms associated with a PCOS belly?
Symptoms of PCOS include a big belly, irregular periods, too much hair, acne, and mood swings. These symptoms often happen together with a big belly.
How can I distinguish a PCOS belly from a pregnant belly?
A PCOS belly grows slowly over time. A pregnant belly grows faster. A PCOS belly is mostly in the belly area. A pregnant belly is more spread out.
What is the connection between PCOS and insulin resistance?
Insulin resistance is a big part of PCOS. It makes blood sugar levels go up. This leads to more fat, especially in the belly.
How can I effectively manage PCOS belly fat?
To manage PCOS belly fat, eat a low-glycemic diet. Do exercises that target the belly. You might also need medical help to balance hormones and improve insulin sensitivity.
How does alcohol consumption affect PCOS symptoms?
Drinking alcohol can make PCOS symptoms worse. It can cause weight gain and more belly fat. It also messes with hormones and insulin levels.
What are some effective exercises for targeting PCOS belly fat?
Good exercises for PCOS belly fat include strength training and cardio. These help burn belly fat. Eating right is also important.
What are some natural remedies and supplements that may help with PCOS management?
Natural remedies like myo-inositol can help with PCOS. Vitamins like vitamin D and chromium also support hormone balance and metabolism.